Summary by Geopolist | Istanbul Center for Geopolitics:
The article investigates how emotions, particularly those related to nationalism and national identity, might exacerbate confrontations via social media, putting pressure on leaders to escalate crises. Public emotions, including humiliation and wrath, can be amplified by social media platforms like Weibo in the context of China. This phenomenon of emotional contagion, or the peer-to-peer spread of feelings, significantly impacts political behaviour, prompting leaders to react more aggressively to evade a potential backlash. Even in authoritarian regimes such as China, leaders risk losing legitimacy if they oppose nationalist sentiment, complicating de-escalation during crises.
Key Points
Emotional Contagion: Emotions circulate within social networks, shaping personal actions and collective reactions. The peer-to-peer sharing plays a vital role in catalyzing collective political action, particularly when a common national identity is at stake.
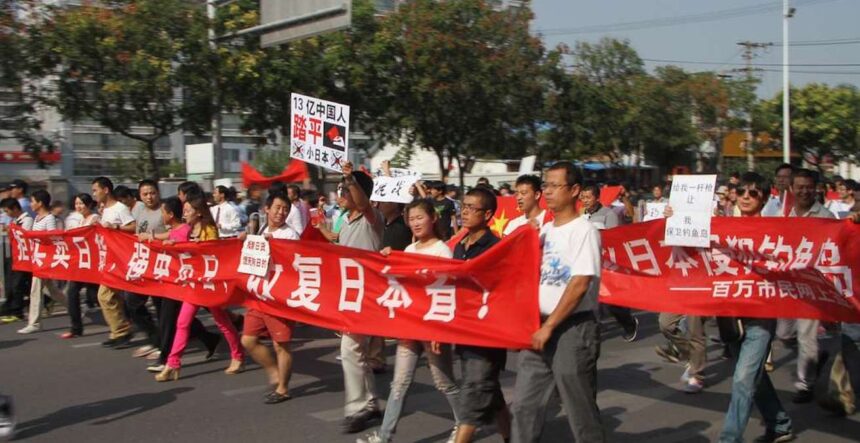
Nationalism as a Catalyst: Nationalist narratives, frequently grounded in historical grievances, may remain inactive and then suddenly surge in reaction to external influences. The dispute over the Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands sparked extensive anti-Japan protests in China in 2012, demonstrating how a longstanding issue can quickly turn politically charged.
Social Media’s Role: Platforms such as Weibo enable swift emotional contagion, allowing feelings like anger or humiliation to spread rapidly among users. This process influences policy preferences, including a tendency to support assertive positions in international conflicts.
The influence on leaders: Even authoritarian figures in nations such as China cannot escape the pressures created by public sentiment. They might encounter significant pressures to align with nationalist sentiment, as not doing so could jeopardize their legitimacy and potentially their existence.
Perilous Intensification: In situations such as Taiwan, societal demands may constrain a leader’s capacity to reduce tensions. In times of crisis, heightened public sentiment can compel leaders to engage in confrontations they would typically seek to evade, complicating any attempts to retreat.
Propaganda Backfire: Although governments employ stories of national humiliation to garner support, these narratives have the potential to escalate uncontrollably. When the emotions of citizens run high, they may advocate for more forceful measures than the government had planned, leading to a conflict between escalating the situation or dealing with potential backlash.
In summary, it indicates that grasping the impact of emotion and social media on international relations is essential, as they can affect state behaviour in unforeseen and possibly perilous manners.
Read the full article here.